WHAT IS PASSIVE VOICE?
Active Voice: “The subject” does the action. “The subject ” has the main role. “The subject” is important than “the verb” and “the object.” The subject takes responsibility or blames.
Passive Voice = “The object” receives the action. “The object and verb” has the main role. “The verb” is more important than “the object,” but “the subject” has no importance. The subject does not want to take responsibility or blame.
There is a difference between Active and Passive Voice. Let’s look up!
Note – We do not need to mention “Subject as an agent” in the passive voice because there are so many reasons to make a passive voice. We use Passive Voice When –
- When “The Subject” does not take responsibility.
- When “The Subject” does not take the blame.
- When we do not give credit to “The Subject” of their action.
- When we focus on “The Action or Verb,” not on “The Subject.”
- When we do not know “The Subject.”
- And so many more reasons.
How To Convert Active Voice Into Passive Voice?
Passive Voice Instructions = You need to follow all the instructions carefully before using “Passive Voice.” When we convert “Active Voice” into “Passive Voice,” there is no difference in the definition of “the Passive Voice.” Let’s follow all these instructions to understand “Passive Voice.”
Active Voice —-> Passive Voice
1. By + Subject as Object – You move the ‘Subject’ in place of ‘Object’ in a sentence. The subject works as an agent now. We add “By” before the “Subject as an agent.” “The Subject Pronoun” converts into the same “Object Pronoun.”
Let’s see = To learn more about the “Subject and Object” pronoun, you can click on the button
–
Subject Pronoun | Object Pronoun |
| He | Him |
| She | Her |
| It | It |
| You | You |
| I | Me |
| We | Us |
| They | Them |
| Who | Whom |
| Noun = Cat, Dog, Man, Woman, Friend, Teacher, or Sister, etc. | Noun = Cat, Dog, Man, Woman, Friend, Teacher, or Sister, etc. |
| Nouns = Cats, Dogs, Men, Women, Friends, Teachers, Sisters, etc. | Nouns = Cats, Dogs, Men, Women, Friends, Teachers, or Sisters, etc. |
e.g. –
- He runs the company. (Active Voice = General truth and routine)
- The company is run by him. (Passive Voice = General truth and routine. “He” converts into “Him.” The subject “He” moves in place of the object.)
- I am delivering a pizza. (Active Voice = Work progress)
- A pizza is being delivered by me. (Passive Voice = Work progress. “I” converts into “Me.” The subject “I” moves in place of the object. )
- A man cooked the food. (Active Voice = Completed Action)
- The food was cooked by a man. (Passive Voice = Completed Action. “A man” converts into “A man.” The subject “A man” moves in place of the object.)
2. Object as a Subject – You move the “Object” in place of the “Subject” in the sentence. The object is a receiver. “The Object Pronoun” converts into the same “Subject Pronoun,” but it is not a subject. I repeat, “It is not a subject.”
Let’s see =
e.g. –
- He forces us. (Active Voice = General truth and routine.)
- We are forced by him. (Passive Voice = General truth and routine. “Us” converts into “We.” The object “Us” moves in place of the subject. “We” is not a subject here. “We” is a receiver, not a doer.)
- They killed her. (Active Voice = Completed action.)
- She was killed by them. (Passive Voice = Completed action. “Her” converts into “She.” The object “Her” moves in place of the subject. “She” is not a subject here. “She” is a receiver, not a doer. )
- I can win the race. (Active Voice = To show ability.)
- The race can be won by me. (Passive Voice = To show ability. “The race” converts into “The Race.” The object “Race” moves in place of the subject. “The race” is not a subject here. “The race” is a receiver, not a doer.)
3. The Verb – You move the “Subject” in place of the “Object” and “the object” in place of the “subject.” The verb changes according to the new “Object.” If the new object is singular, the verb will be singular as well. If the new object is plural, the verb will be plural as well.
Let’s see =
e.g. –
- He is controlling them. (Active Voice = Work progress.)
- They are being controlled by him. (Passive Voice = Work progress. The subject “He'” moves in place of the object. “He” converts into “Him.” The object “They” moves in place of the subject. “Them” converts into “They.” “They” is plural, so the verb “is” changes into “are.”)
- We were making the food. (Active Voice = Completed progress.)
- The food was being made by us. (Passive Voice = Completed progress. The subject “We” moves in place of the object. “We” converts into “Us.” The object “Food” moves in place of the subject. “The food” converts into “The food.” “Food” is singular, so the verb “were” changes into “was.”)
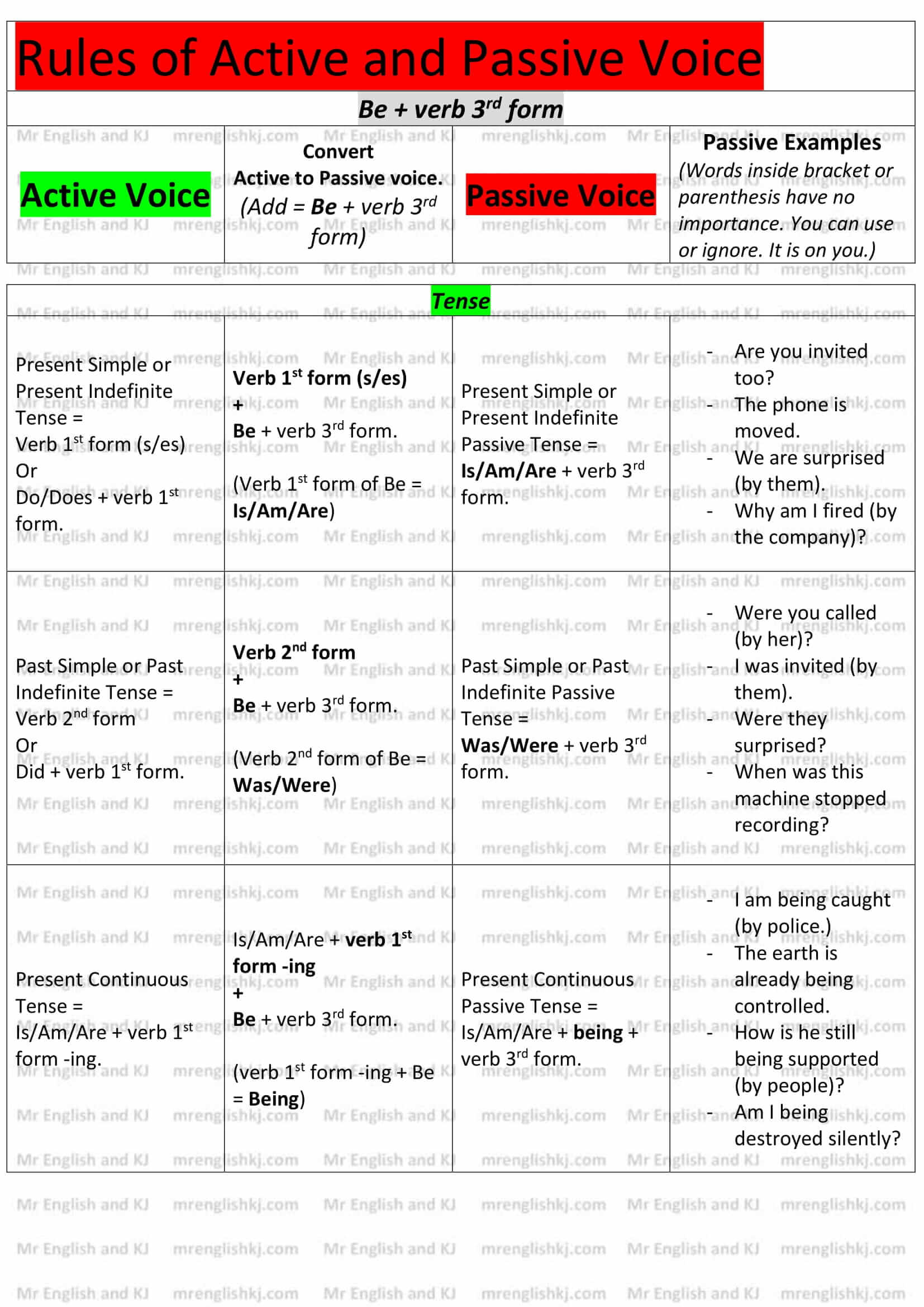
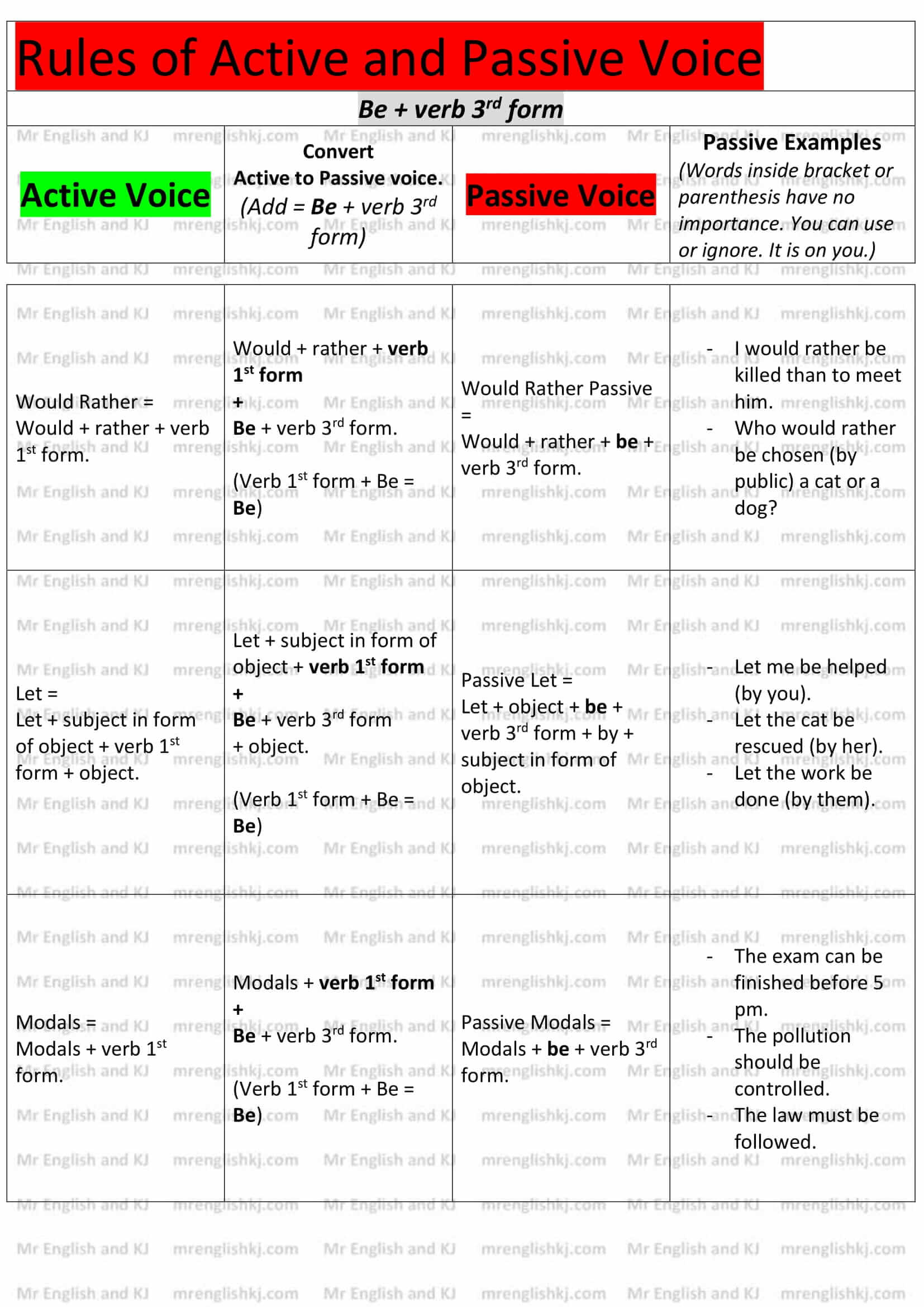
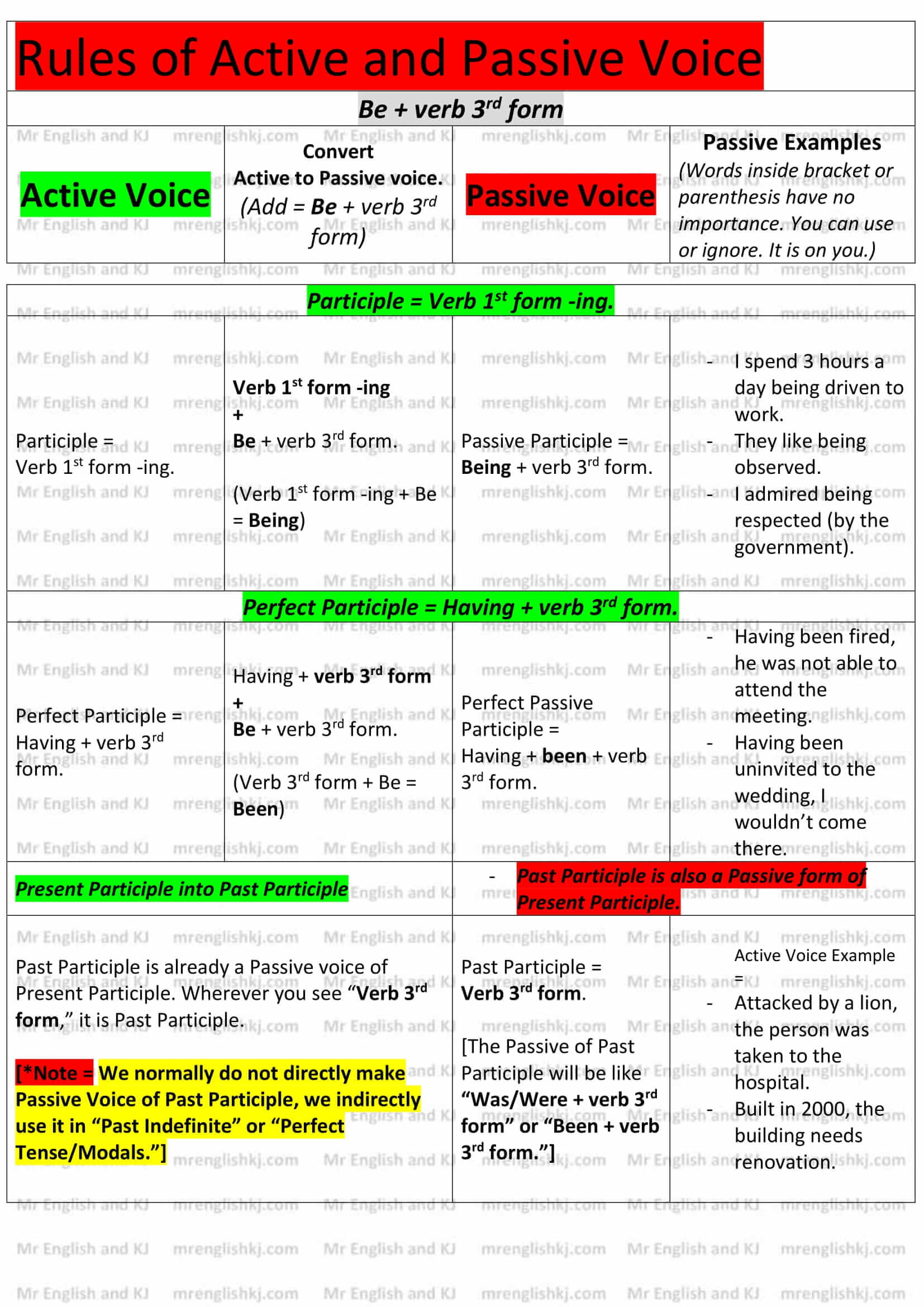
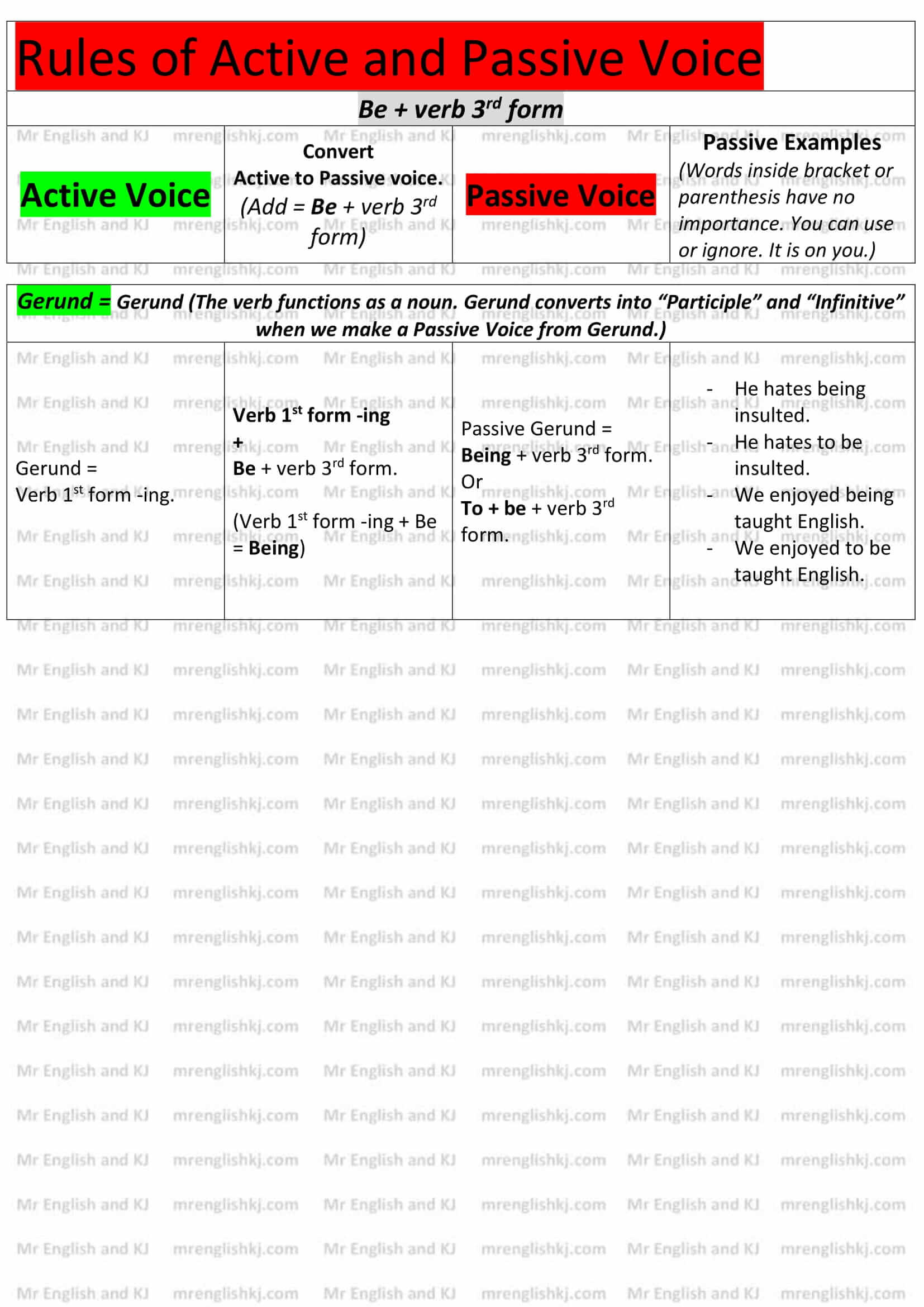
4. Be + Verb 3rd form – A passive voice is all about “Be + verb 3rd form.” We use it in every passive sentence. Whenever we convert “Active Voice” into “Passive Voice,” we add “Be + verb 3rd form.”
Let’s see =
e.g. –
- He is helping her. (Active Voice = Work progress.)
- She is being helped by him. (Passive Voice = Work progress. “Being + helped” = “Be + verb 3rd form.”)
- I will not ask them next time. (Active Voice = Possibility or Prediction.)
- They will not be asked by me next time. (Passive Voice = Possibility or Prediction. “Be + asked” = “Be + verb 3rd form.”)
- We can pass the exam. (Active Voice = To show ability.)
- The exam can be passed by us. (Passive Voice = To show ability. “Be passed” = “Be + verb 3rd form.”)
5. It and There – We use “It and There” in place of “Object as a Subject.” When there is no object in the sentence, we use “It and There” to replace the object. When we do not want to use the object as a subject in passive voice, we use “It and There.” We mostly use “It.”
Let’s see =
e.g. –
- He plays daily. (Active Voice = General truth or routine.)
- It is played daily by him. (Passive Voice = General truth or routine. There is no object in the Active sentence, so we use “It.”)
- I did yesterday. (Active Voice = Completed action.)
- It/There was done yesterday by me. (Passive Voice = Completed action. There is no object in the Active sentence, so we use “It or There.”)
6. Two Objects – When there are two objects in the “Active” sentence, we can use any object in place of “Object as Subject.”
Let’s see =
e.g. –
- Would you lend me a pen? (Active Voice = Formal and Polite Question. “Me” is an object. “Pen” is also an object.)
- Would a pen be lent to me by you? (Passive Voice = Formal and Polite Question. “Pen” moves from object to “Object as a subject.”)
Or
- Would I be lent a pen by you? (Passive Voice = Formal and Polite Question. “Me” converts into “I.” “I” is in a place of “Object as a subject.”)
- He explains this to them. (Active Voice = General truth or routine. “This” is an object. “Them” is also an object.)
- This is explained to them by him. (Passive Voice = General truth or routine. “This” moves from object to “Object as a subject.”)
Or
- They are explained this by him. (Passive Voice = General truth or routine. “Them” converts into “They.” “They” is in a place of “Object as a subject.”)
7. Prepositional Phrase – We only switch “Object” in place of “Subject.” We mostly do not move “Prepositional Phrase” in passive voice. A prepositional phrase always starts with a Preposition, and it is not a receiver. When there is no object in a sentence, we use “It” as an object in place of the subject.
Let’s see =
e.g. –
- He studies in the room. (Active Voice = General truth or routine. “In the room” is not an object.)
- It is studied in the room by him. (Passive Voice = General truth or routine. “He” converts into “Him.” There is no object, so we use “It.”)
- We should go to the park sooner. (Active Voice = To express advice. “To the park” is not an object.)
- It should be gone to the park sooner by us. (Passive Voice = To express advice. “We” converts into “Us.” There is no object, so we use “It.”)
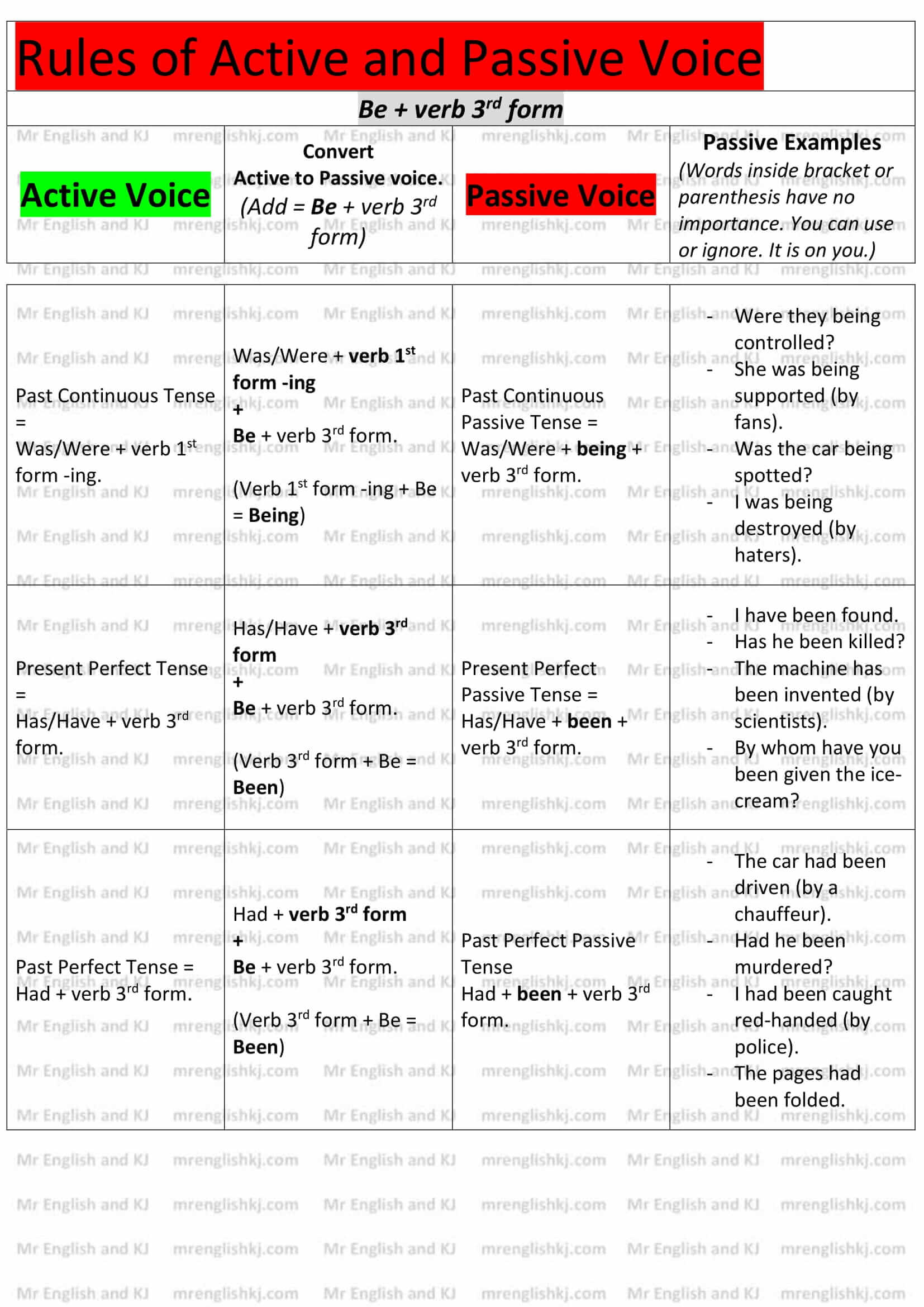
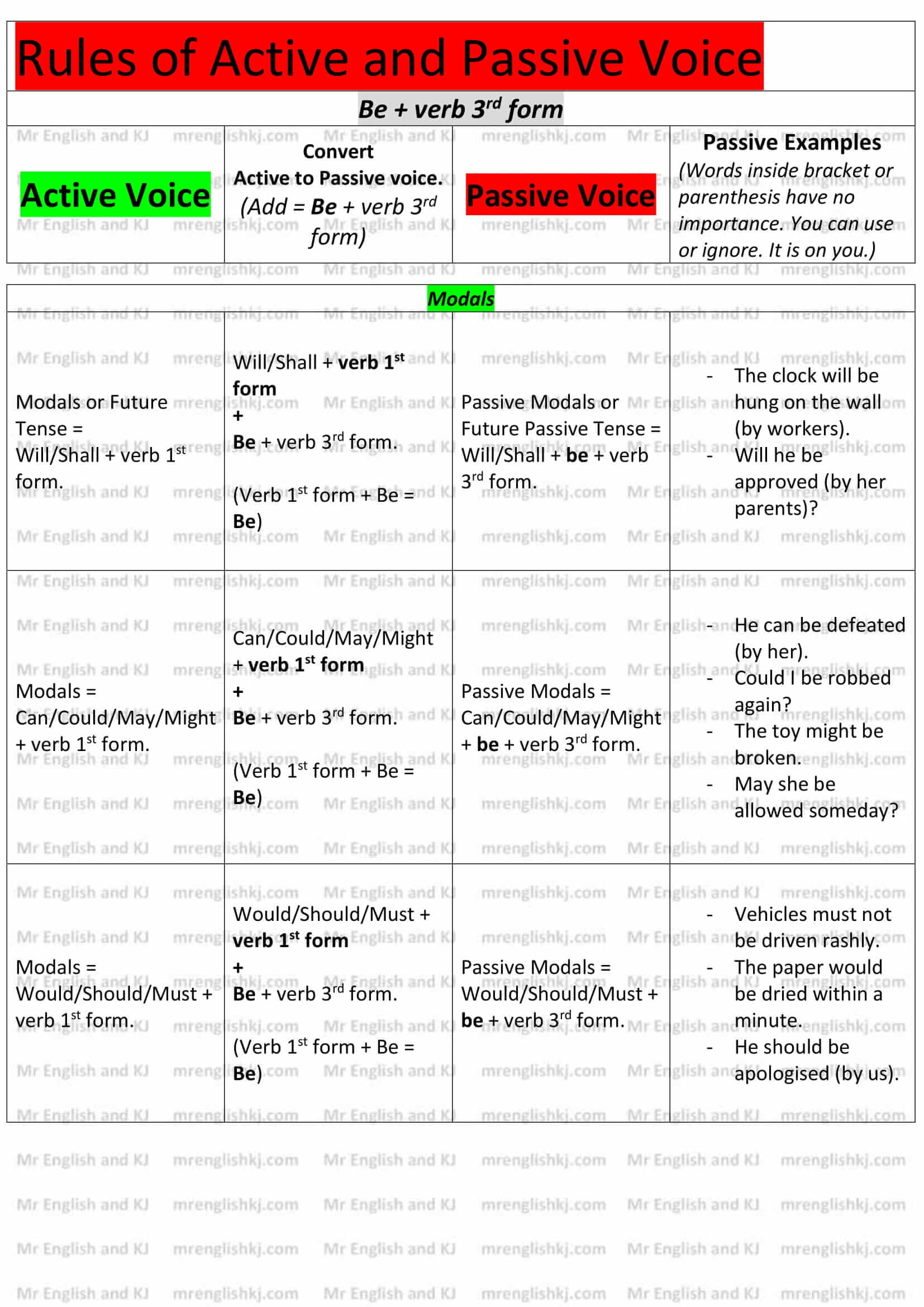
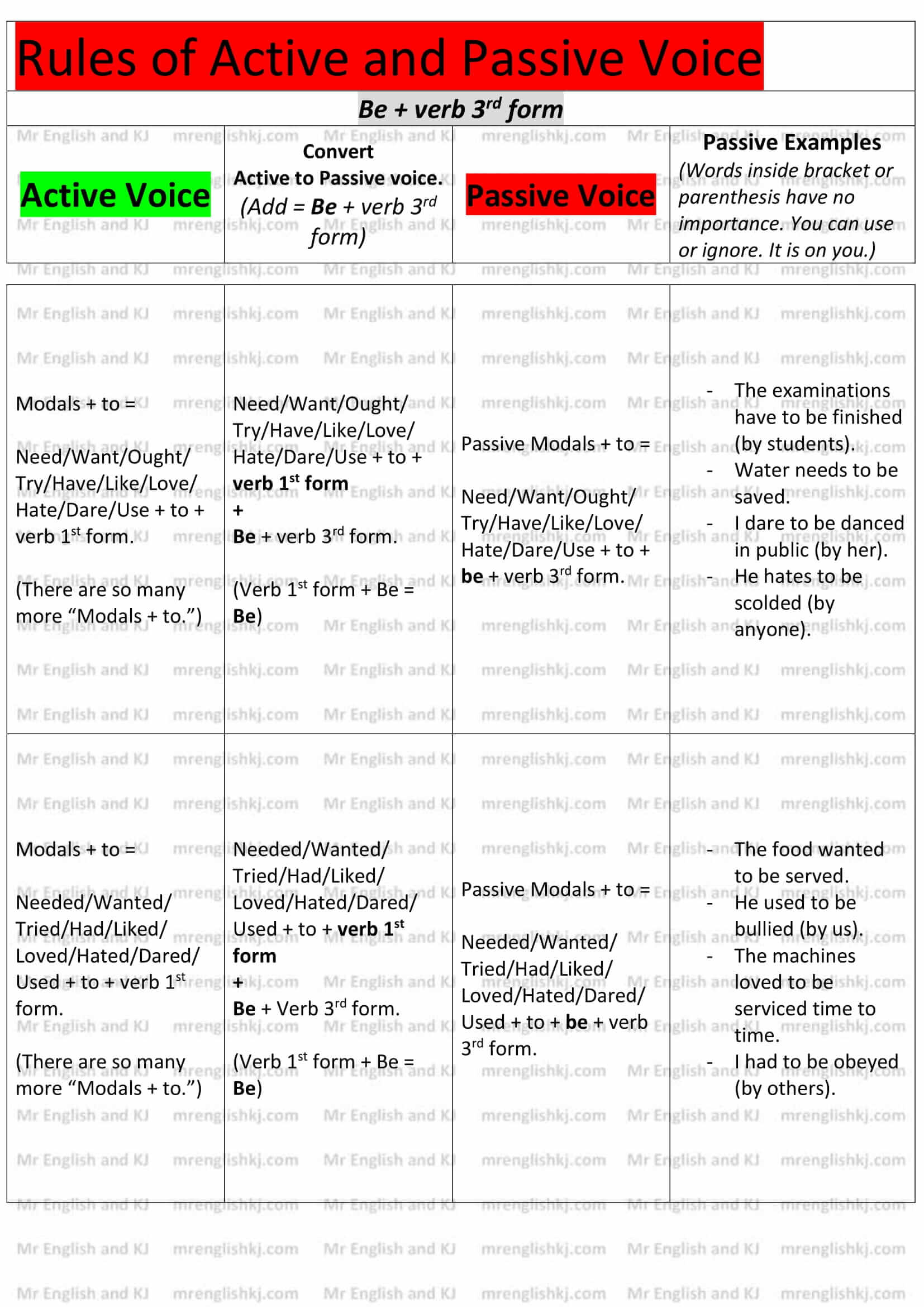
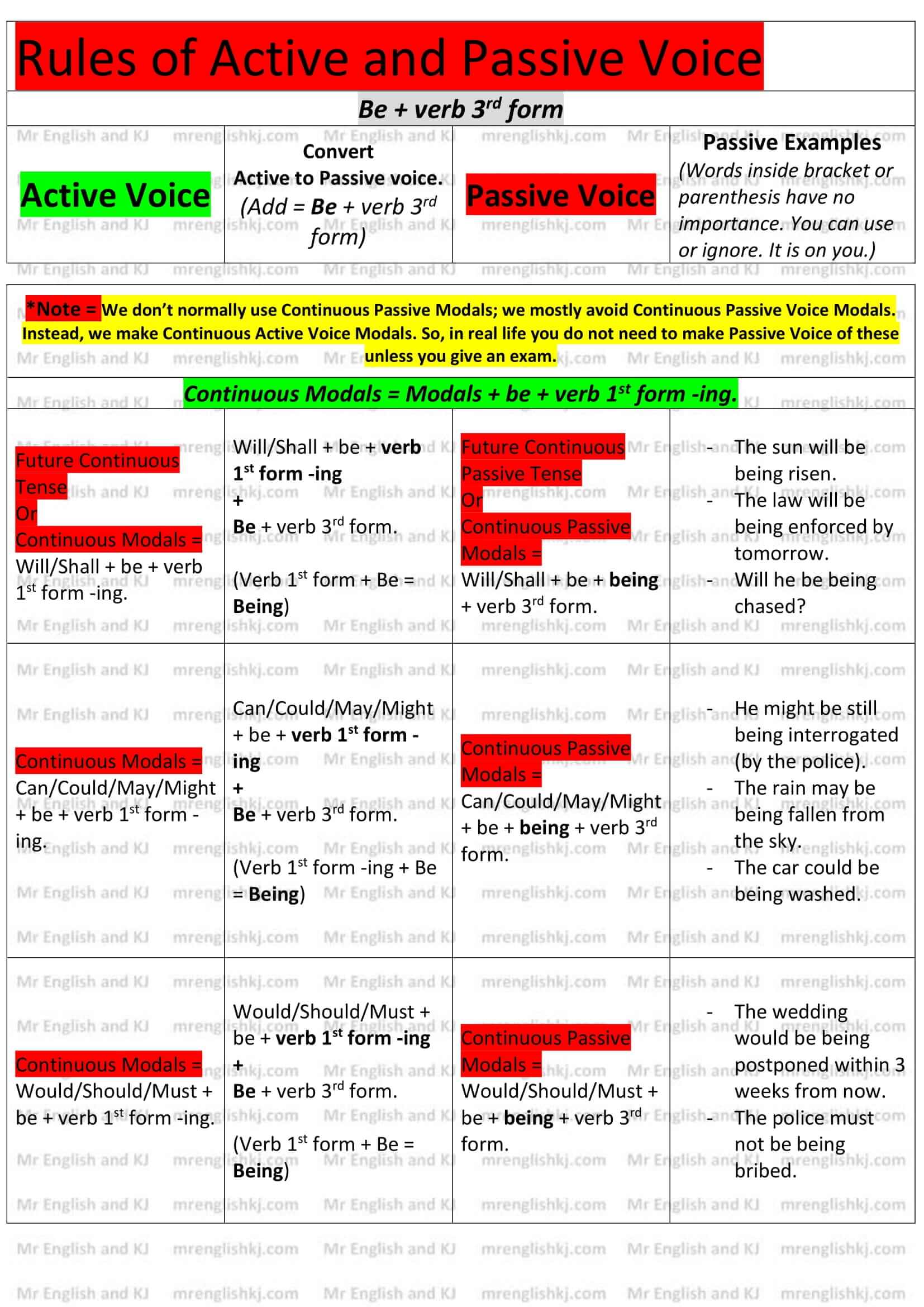
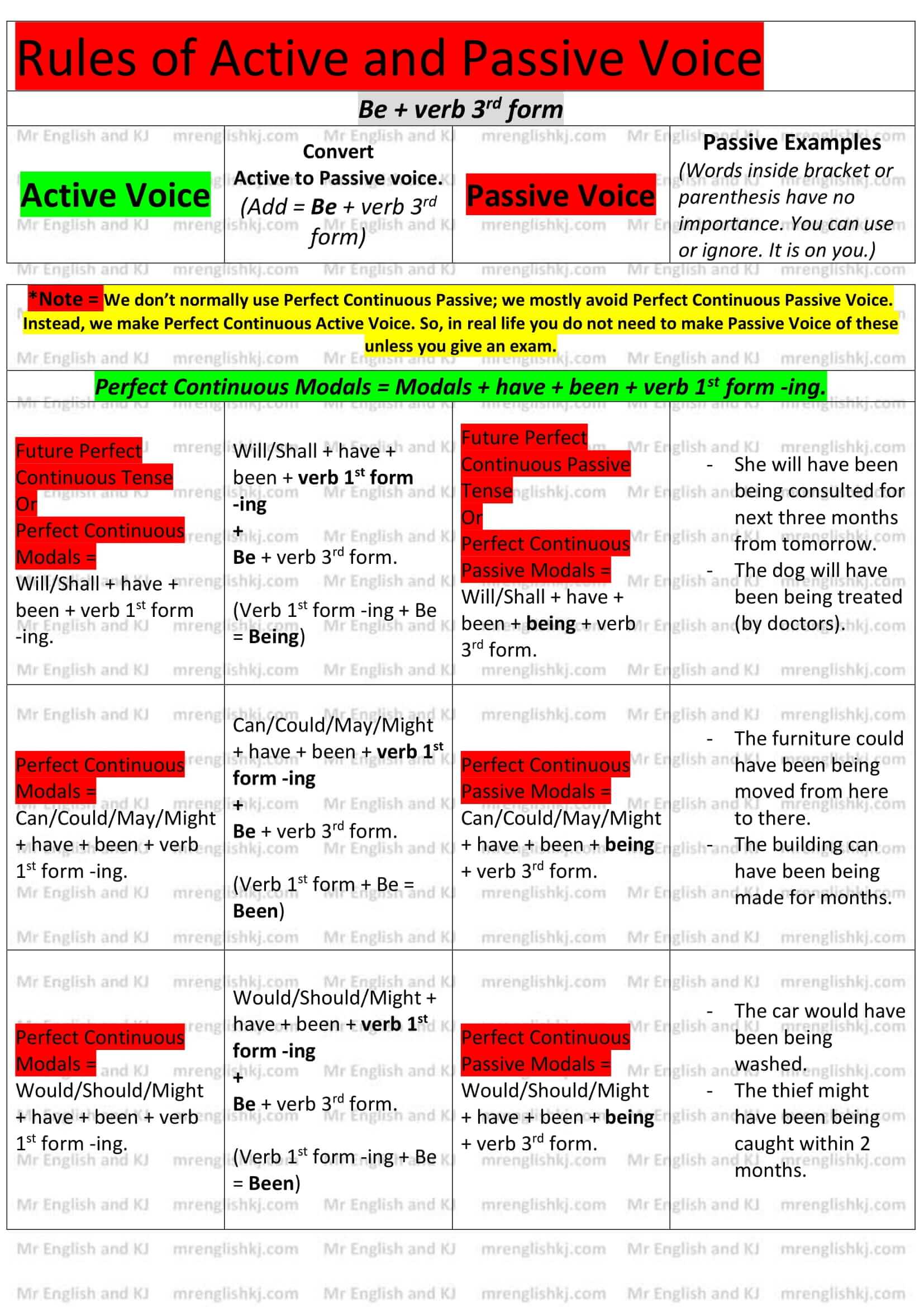
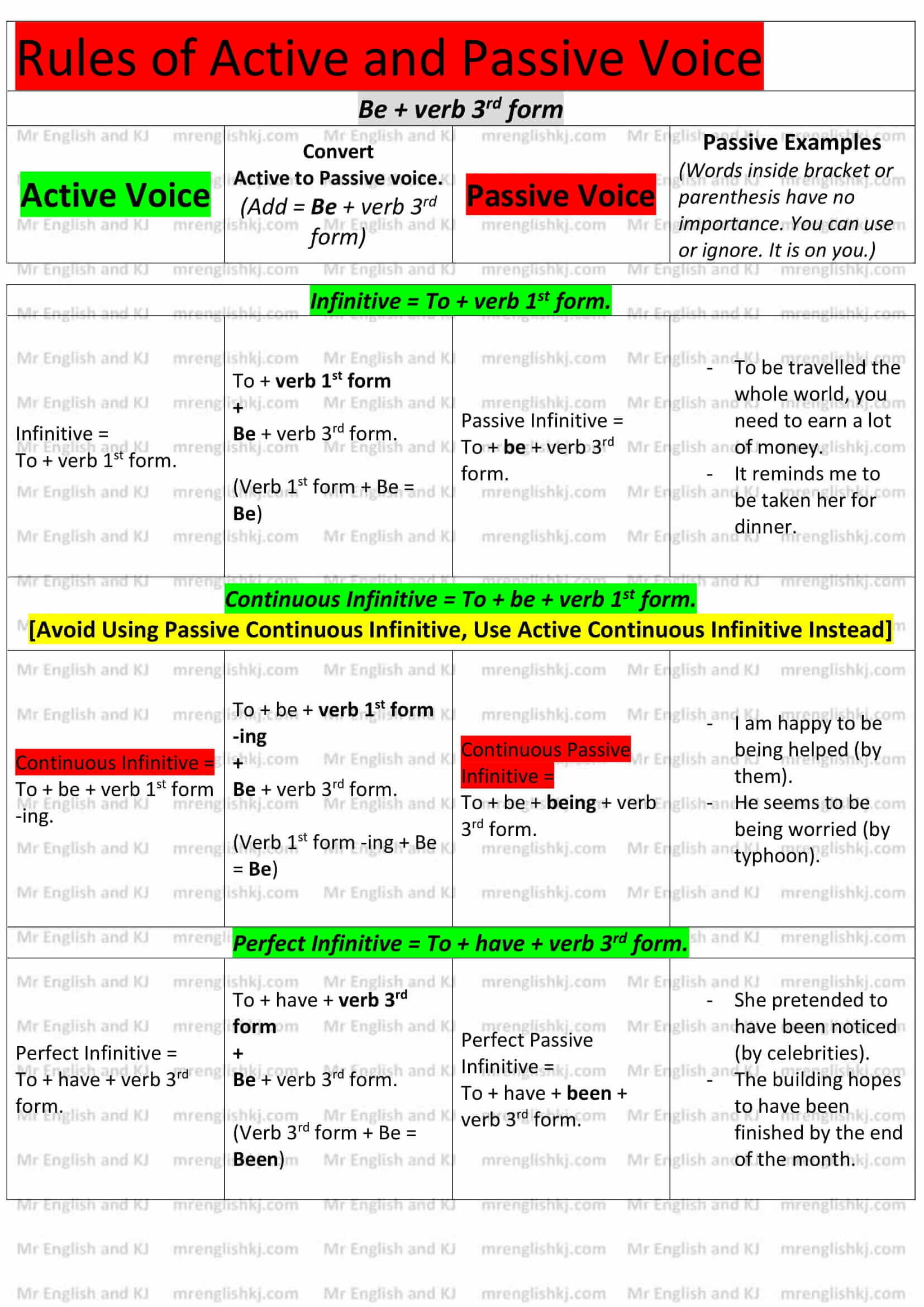
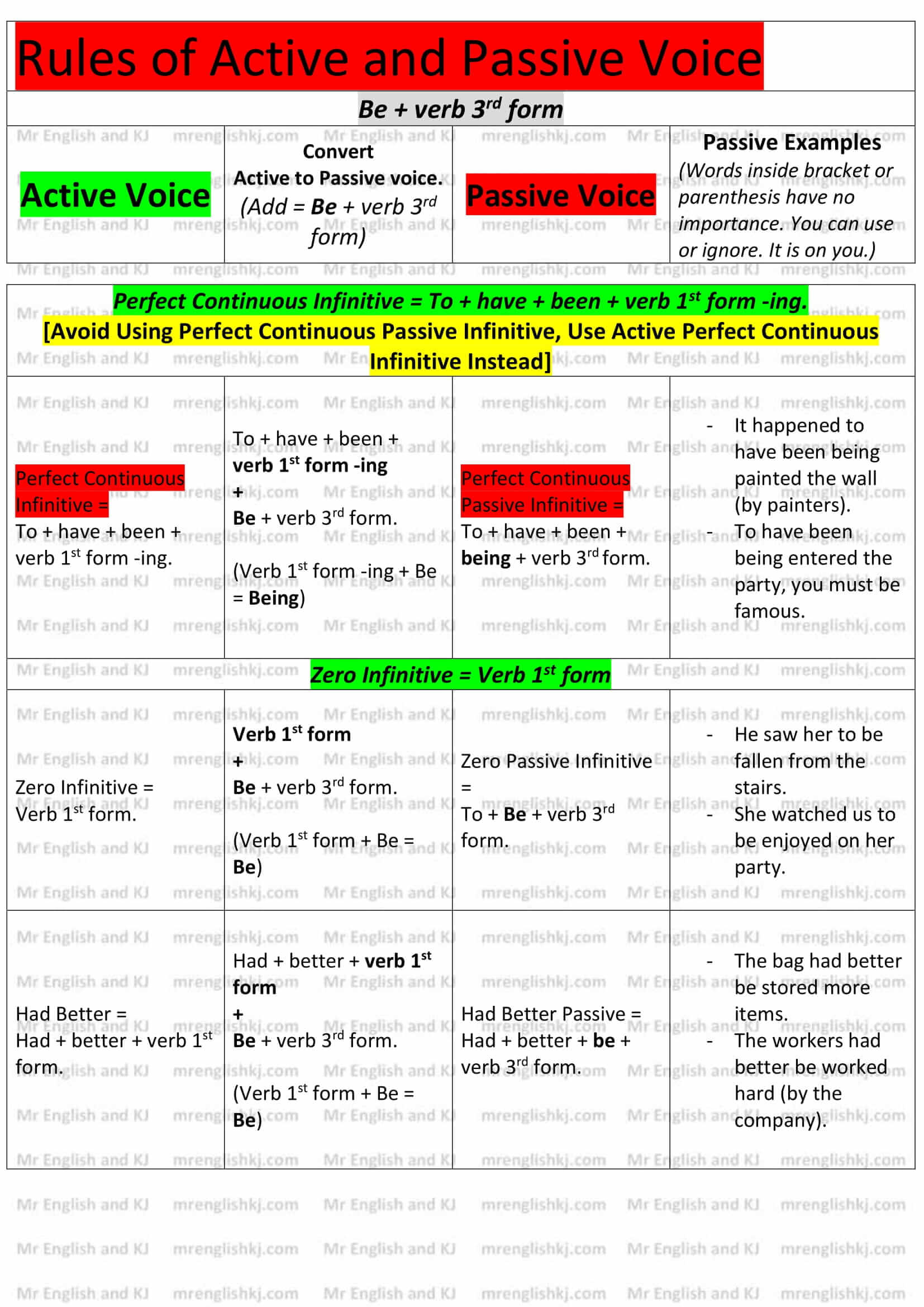
Rules of Passive Voice = There, we learn to convert “Active Voice” rules into “Passive Voice” rules. Let’s take a look!
You can not cram all these rules, can you?
Let’s understand all these rules to make it easy to remember for you! There are few steps that we take to understand Passive Voice rules.
There are a lot of examples of Active to Passive Voice on the next page. Let’s go to the 2nd page!