Pronoun
What is Pronoun? – It is a combination of 2 words ‘Pro + Noun,” which means, a short and better version of ‘Noun.’ We put ‘Pronoun’ in place of ‘Noun’ so that makes it easier to speak and write the sentence.
For example –
- Noun – Earth is the home of various species. Various species live together on Earth. Earth has life. Various species should care for the Earth.
- Pronoun – Earth is the home of various species. All species live together on it. It has life. We should care for it.
Only on these sentences! – We = various species.
Only on these sentences! – It = Earth.
Only on these sentences! – All = various.
The pronoun is a “Parts of Speech.” Now you can see that ‘the pronoun’ makes it easy to use. The sentences are short and easier to speak and write. Let’s Learn clearly about ‘the Pronoun!’
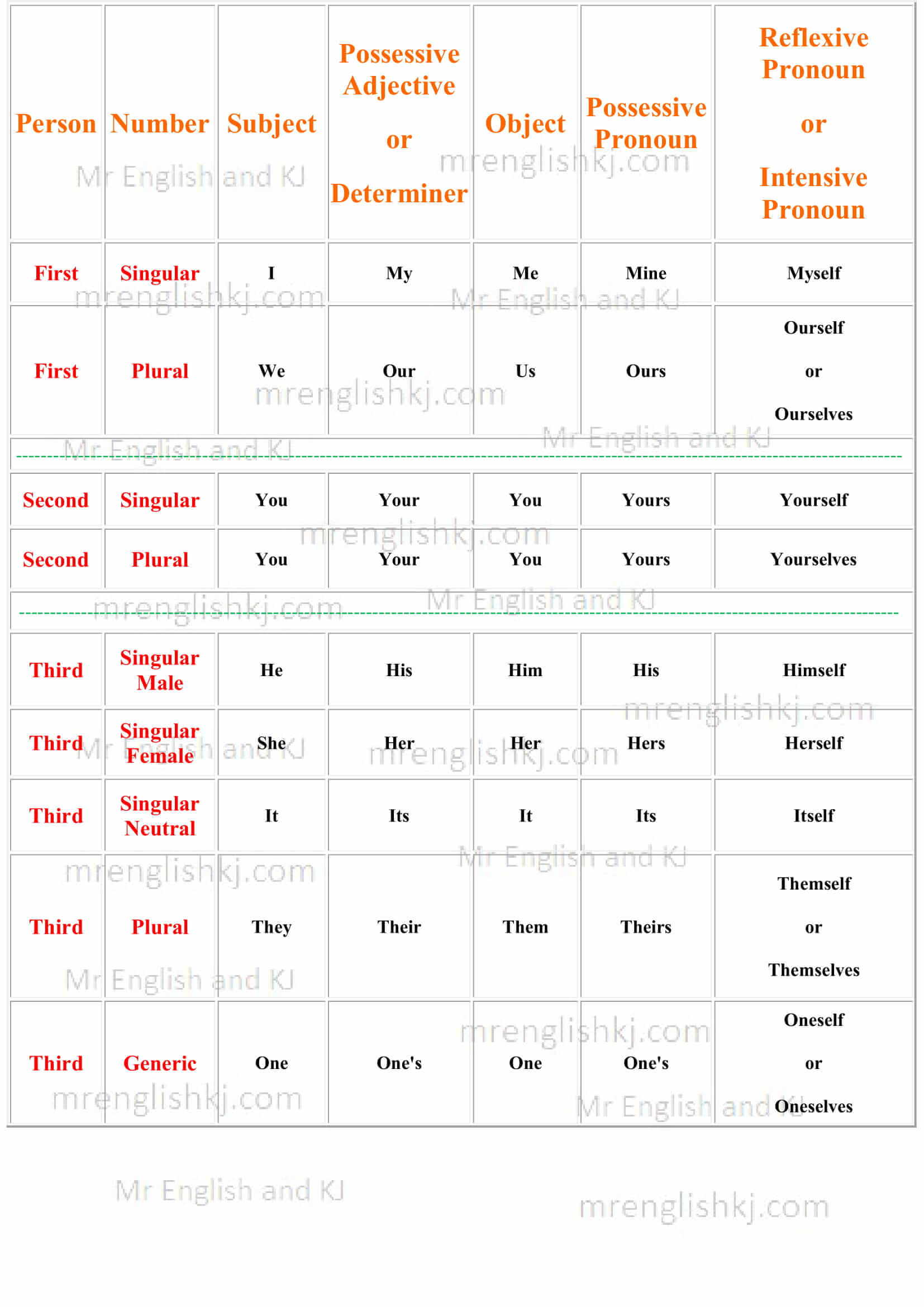
Chart of Pronoun
[su_button url=”https://mrenglishkj.com/wp-content/uploads/2021/01/Pronoun-Chart.pdf” target=”blank” style=”3d” background=”#fd374c” color=”#ffffff” size=”10″ center=”yes” radius=”20″ desc=”Pronoun Chart Pdf File”]Click to Download “List of Pronoun” Pdf File[/su_button]
Person –
- First-person = The Speaker. (‘First Person’ speaks or writes the sentence.)
- Second Person = The Listener. (‘Second Person’ listens to the sentence.)
- Third Person = Neither The Speaker nor The Listener.
(Third Person = To whom ‘The First Person’ talks or writes about – The First Person talks or writes about ‘The Third Person’ and ‘The Second Person only listens about ‘The Third Person.”
- Generic = It can be ‘First Person,’ ‘Second Person,’ or ‘Third Person.’ Generic means general.
Number –
- Singular = One.
- Plural = More than one.
- Generic = It can be ‘One’ or ‘More than one.’ Generic means general.
Subject –
- A subject is a ‘Doer’ (Agent of an action). The person who does any act or expresses any action. We call him or her ‘Subject.’ This definition only works when there is a ‘Verb’ in a sentence.
- When the sentence is about anyone or anything which has a main role in the sentence, we call it ‘Subject.’ This definition only works when there is no ‘Verb’ in a sentence.
or
- When we give information about anyone or anything in the sentence that anyone or anything in the sentence is the ‘Subject.’ This definition only works when there is no ‘Verb’ in a sentence.
e.g. –
- He runs fast. (The doer. ‘Runs’ is a verb. ‘Fast’ is an adverb.)
- He is happy. (Giving information about ‘He.’ ‘Happy’ is an adjective.)
- They are grieving. (The doer. ‘Grieving’ is a verb.)
- They are greedy. (Giving information about ‘They.’ ‘Greedy’ is an adjective.)
- I can jump. (The doer. ‘Jump’ is a verb.)
- I can be jumpy. (Giving information about ‘I.’ ‘Jumpy’ is an adjective.)
Object –
- An object is a ‘Receiver’ which/who receives work, expression of work, or details in a sentence. When anyone or anything receives an act, expression of an act, or information, it is an ‘Object.’
e.g. –
- I know him. (‘Him’ receives the expression of an act. ‘I’ is a doer. ‘I’ does the expression of an act which is ‘Know’ and ‘Him’ receives the expression of an act.)
- I am with her. (‘Her’ receives the information. ‘I’ is the main role. The information is about ‘I’ and ‘Her’ receives the information.)
- He brings food for me. (‘Me’ receives the act. ‘He’ is a doer. ‘He’ does the act which is ‘Bring’ and ‘Me’ receives the act.)
- X and Y fight to them. (‘Them’ receives the act. ‘X and Y’ are doers. ‘X and Y’ does the act which is ‘Fight’ and ‘Them’ receives the act.)
- They are with us. (‘Us’ receives the information. ‘They’ is the main role. The information is about ‘They’ and ‘Us’ receives the information.)
Possessive Adjective –
- We use this pronoun to show belongingness and ownership to a noun or nouns. This pronoun always comes with a noun or nouns.
- Possessive Adjective can become ‘Subject’ and ‘Object’ both. It can come in the place of ‘Subject’ and ‘Object.’
e.g. – His, Her, My, Our, Your, or Their, etc. + noun or nouns
- I have his car. (The car belongs to ‘His’ which is ‘He.’ ‘His car’ is a possessive adjective in place of ‘Object.’)
- His cars are amazing. (The cars belong to “His” which is ‘He.’ ‘His cars’ is a possessive adjective in place of ‘Subject.’)
- Whose chair is this? (The chair belongs to ‘Whose’ which is ‘Who.’ ‘Whose chair’ is a possessive adjective in place of ‘Object.’)
- They have my three pens. (The three pens belong to ‘My’ which is ‘I.’ ‘My three pens’ is a possessive adjective in place of ‘Object.’)
- My house is your house. (The house belongs to ‘My’ and ‘Your’ which are ‘I’ and ‘You.’ ‘My house’ is a possessive adjective in place of ‘Subject.’ ‘Your house’ is a possessive adjective in place of ‘Object.’)
Possessive Pronoun –
- We use this pronoun to show belongingness and ownership to a noun or nouns. This pronoun does not come with a noun or nouns. It always comes alone without a noun or nouns but we only use this pronoun when we already know about the noun.
- Possessive Pronoun can become ‘Subject’ and ‘Object’ both. It can come in the place of ‘Subject’ and ‘Object.’
For example –
- Our car = Ours.
- Our car is beautiful. There is ours (There is our car). Where is your car?
Answer – Mine is there (My car is there).
You can see that we already mentioned ‘our car’ so we do not need to mention it again. That time we use ‘Possessive Pronoun’ when we already know about the noun or we already mentioned the noun.
e.g. –
- I have his car. His car is red. There is his. (The car belongs to ‘His’ which is ‘He.’ ‘His’ is a possessive pronoun in place of ‘Object.’)
- His cars are amazing. His look is elegant. (The cars belong to “His” which is ‘He.’ ‘His’ is a possessive pronoun in place of ‘Subject.’)
- Whose chair is this? I repeat – Whose is this? (The chair belongs to ‘Whose’ which is ‘Who.’ ‘Whose’ is a possessive pronoun in place of ‘Object.’)
- They have my three pens. These are mine, give them to me. (The three pens belong to ‘My’ which is ‘I.’ ‘Mine’ is a possessive pronoun in place of ‘Object.’)
- My house is your house or Mine is yours. (The house belongs to ‘My’ and ‘Your’ which are ‘I’ and ‘You.’ ‘Mine’ is a possessive pronoun in place of ‘Subject.’ ‘Yours’ is a possessive pronoun in place of ‘Object.’)
Reflexive Pronoun –
- This pronoun shows a reflection of the subject. It uses to give more emphasis or force on the subject.
- Reflexive means a reflection just like the reflection of a mirror. Reflexive Pronoun is also known as ‘Mirror Pronoun.’ We use one subject twice but using a different word and that second pronoun is the reflection of the first.
- We always use the same Reflexive Pronoun just like the ‘Subject’ that we use to show emphasis
For example –
- For ‘I’ we use ‘Myself.’
- For ‘We’ we use ‘Ourself or Ourselves.’
- For ‘It’ we use ‘Itself.’
- For ‘He’ we use ‘Himself.’
- For ‘They’ we use ‘Themself or Themselves.’
e.g. –
- I myself can do this task. (‘Myself’ is a reflection of ‘I’ which gives more force or emphasis on ‘I’ that ‘I can do this task all alone without any help of others.’)
- He himself helps them. (‘Himself’ is a reflection of ‘He’ which gives more force or emphasis on ‘He’ that ‘He helps them without any help of others.’)
- They themselves finish this work. (‘Themselves’ is a reflection of ‘They’ which gives more force or emphasis on ‘They’ that ‘They finish this work all alone without any help of others.’)
- We ourselves could earn the profit. (‘Ourselves’ is a reflection of ‘We’ which gives more force or emphasis on ‘We’ that ‘We could earn the profit all alone without any help of others.’)
- She herself can achieve anything. (‘Herself’ is a reflection of ‘She’ which gives more force or emphasis on ‘She’ that ‘She can achieve anything all alone without the help of others.’)
Thanks for choosing us!