
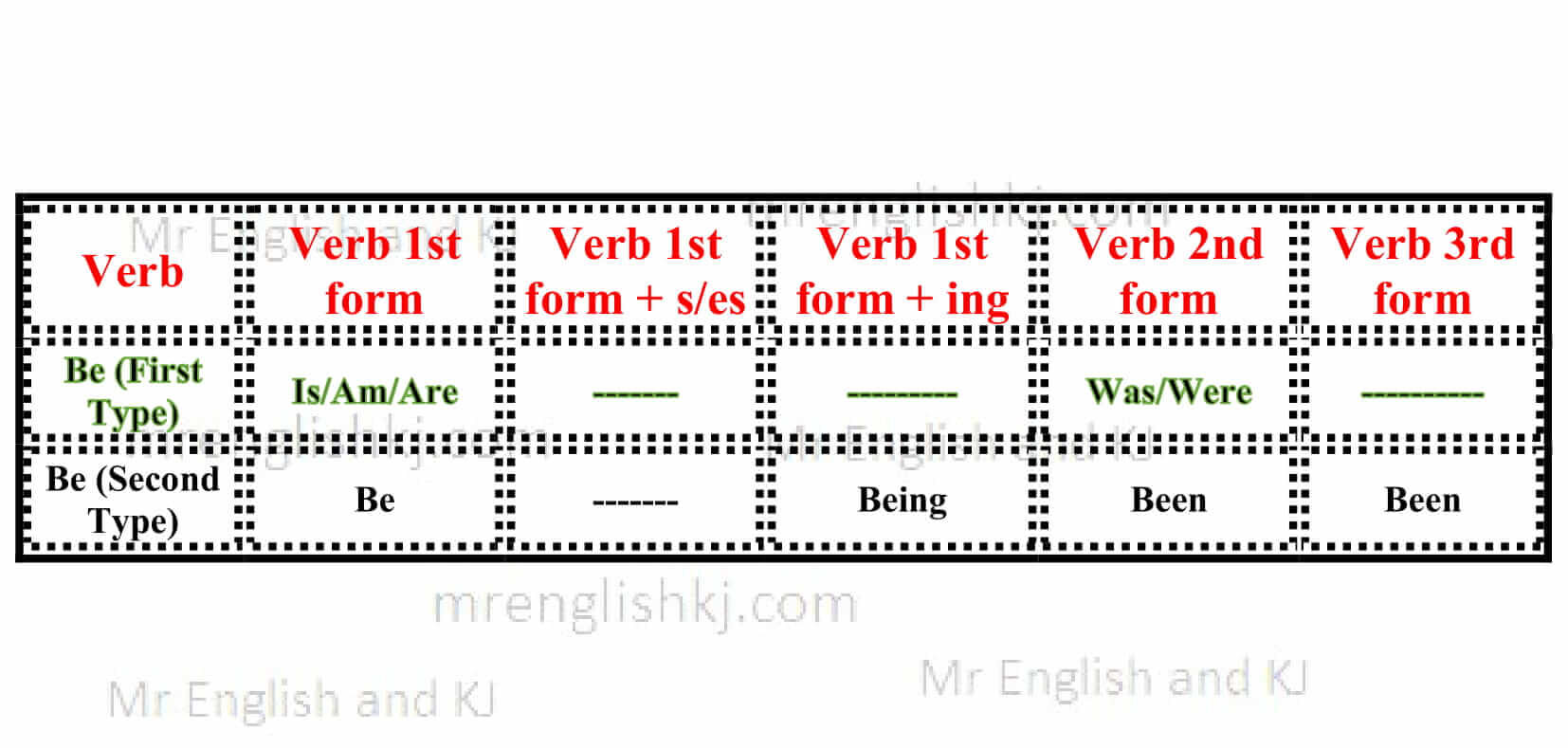
1. We add “Be + verb 3rd form” everywhere in passive voice. “Be” is also a verb, but it has two types.
2. The “Be” first type, we use only for “Present Simple or Present Indefinite Tense” and “Past Simple or Past Indefinite Tense.”
Let’s breakdown it =
- Present Simple or Present Indefinite Tense – Active Voice rule = Verb 1st form (s/es) or Do/Does + Verb 1st form. So, the verb 1st form of “Be” first type is “Is/Am/Are.” We focus on “Verb 1st form,” not on “Do/Does.”
- The passive rule = “Is/am/are + verb 3rd form.” As you can see “Verb 1st form + Be = Is/Am/Are”
- Note One Thing: We always use “Be + verb 3rd form” in passive voice. Finally, the passive rule is “Is/Am/Are + verb 3rd form.”
- Past Simple or Past Indefinite Tense – Active Voice rule = Verb 2nd form or Did + verb 1st form. So, the verb 2nd form of “Be”, first type is “Was/Were.” We focus on “Verb 2nd form,” not on “Did,”
- The passive rule = “Was/Were + verb 3rd form.” As you can see, “Verb 2nd form + Be = Was/Were.”
- Note One Thing: We always use “Be + verb 3rd form” in passive voice. Finally, the passive rule is “Was/Were + verb 3rd form.”
3. “Be’ the second type, we use this rule in every passive voice except “Present and Past Indefinite Tense.” In passive voice, we add “Be + verb 3rd form” everywhere.
Let’s break it down:
- Present Continuous Tense – Active Voice = “Is/Am/Are + verb 1st form + ing,” after this rule, we add “Be + verb 3rd form.” (Verb 1st form -ing + Be = Being)
- Is/am/are + verb 1st form -ing + Be + verb 3rd form = Is/am/are + being + verb 3rd form. (“Be” is a verb 1st form, and we add “ing” after “Be.” It becomes “Being.”)
- Past Perfect Tense – Active Voice = “Had + verb 3rd form,” after this rule, we add “Be + verb 3rd form.” (Verb 3rd form + Be = Been)
- Had + verb 3rd form + Be + verb 3rd form = Had + been + verb 3rd form. (“Be” is a verb 1st form and “3rd form of Be” is “Been.”)
- Modals – Active Voice = “Can/could/may/might/must/should/would/will/shall + verb 1st form,” after this rule, we add “Be + verb 3rd form.” (Verb 1st form + Be = Be)
- Can/could/may/might/should/would/will/shall + verb 1st form + Be + verb 3rd form. (“Be” is a verb 1st form, and “1st form of Be” is also “Be.”)
- In the same way, we can understand all the rules. I suggest you try to elaborate on all the rules by yourself, then it will become easy for you to remember.
E.g. – Active Voice into Passive.
- Active Voice = She only eats salad. (Present Simple or Present Indefinite Tense – General truth and routine. “She ” is a doer.)
- Passive Voice = Salad is only eaten by her. (Present Simple or Present Indefinite Tense – General truth and routine. “Salad” is a receiver. “She” converts into “Her.” “Her” is a doer.)
- Active Voice = Sam does not write a letter. (Present Simple or Present Indefinite Tense – General truth and routine. “Sam” is a doer.)
- Passive Voice = A letter is not written by Sam. (Present Simple or Present Indefinite Tense – General truth and routine. “Letter” is a receiver. “Sam” is a doer.)
- Active Voice = I saw an obstacle. (Past Simple or Past Indefinite Tense – Completed action. “I” is a doer.)
- Passive Voice = An obstacle was seen by me. (Past Simple or Past Indefinite Tense – Completed action. “Obstacle” is a receiver. “I” converts into “Me.” “Me” is a doer.)
- Active Voice = They did not clean the house. (Past Simple or Past Indefinite Tense – Completed action. “They” is a doer.)
- Passive Voice = The house was not cleaned by them. (Past Simple or Past Indefinite Tense – Completed action. “House” is a receiver. “They” converts into “Them.” “Them” is a doer.)
- Active Voice = Ram is buying fruits. (Present Continuous Tense – Work progress. “Ram” is a doer.)
- Passive Voice = Fruits are being bought by Ram. (Present Continuous Tense – Work progress. “Fruits” is a receiver. “Ram” is a doer.)
- Active Voice = Animals are drinking water from the pool. (Present Continuous Tense – Work progress. “Animals” is a doer.)
- Passive Voice = Water is being drunk from the pool by animals. (Present Continuous Tense – Work progress. “Water” is a receiver. “Animals” is a doer.)
- Active Voice = We were celebrating his birthday. (Past Continuous Tense – Completed progress. “We” is a doer.)
- Passive Voice = His birthday was being celebrated by us. (Past Simple or Past Indefinite Tense – Completed progress. “His birthday” is a receiver. “We” converts into “Us.” “Us” is a doer.)
- Active Voice = He was not reading a novel. (Past Continuous Tense – Completed progress. “He” is a doer.)
- Passive Voice = A novel was not being read by him. (Past Continuous Tense – Completed progress. “Novel” is a receiver. “He” converts into “Him.” “Him” is a doer.)
- Active Voice = She has taught him a lesson. (Present Perfect Tense – Completed action. “She” is a doer.)
- Passive Voice = He has been taught a lesson by her. Or A lesson has been taught to him by her. (Present Perfect Tense – Completed action. “Him” converts into “He.” “He” is a receiver. “She” converts into “Her.” “Her” is a doer.)
- Active Voice = He has controlled my mind. (Present Perfect Tense – Completed action. “He” is a doer.)
- Passive Voice = My mind has been controlled by him. (Present Perfect Tense – Completed action. “My mind” is a receiver. “He” converts into “Him.” “Him” is a doer.)
- Active Voice = Radha had solved the mystery. (Past Perfect Tense – Completed action. “Radha” is a doer.)
- Passive Voice = The mystery had been solved by Radha. (Past Perfect Tense – Completed action. “Mystery” is a receiver. “Radha” is a doer.)
- Active Voice = The government had ruined everything. (Past Perfect Tense – Completed action. “Government” is a doer.)
- Passive Voice = Everything had been ruined by the government. (Past Perfect Tense – Completed action. “Everything” is a receiver. “Government” is a doer.)
- Active Voice = We cannot finish it. (Modals – To express ability. “We” is a doer.)
- Passive Voice = It cannot be finished by us. (Modals – To express ability. “It” is a receiver. “We” converts into “Us.” “Us” is a doer.)
- Active Voice = Will they meet her someday? (Modals or Future Tense – To ask possibility. “They” is a doer.)
- Passive Voice = Will she be met by them someday? (Modals or Future Tense – To ask possibility. “Her” converts into “She.” “Her” is a receiver. “They” converts into “Them.” “Them” is a doer.)
- Active Voice = I should apologize. (Modals – To express advice. “I” is a doer.)
- Passive Voice = It should be apologized by me. (Modals – To express advice. There is no object, so we use “It.” “It” is a receiver. “I” converts into “Me.” “Me” is a doer.)
- Active Voice = Rosy will replace flowers. (Modals or Future Tense – To express possibility. “Rosy” is a doer.)
- Passive Voice = Flowers will be replaced by Rosy. (Modals or Future Tense – To express possibility. “Flowers” is a receiver. “Rosy” is a doer.)
- Active Voice = I can win the race. (Modals – To express ability. “I” is a doer.)
- Passive Voice = The race can be won by me. (Modals – To express ability. “Race” is a receiver. “I” converts into “Me.” “Me” is a doer.)
- Active Voice = It may rain. (Modals – To express possibility. There is no subject in a sentence, so we use “It.”)
- Passive Voice = It may be rained. (Modals – To express possibility. There is no object in a sentence, so we use “It.”)
- Active Voice = Might we lose the game? (Modals – To ask the least possibility. “We” is a doer.)
- Passive Voice = Might the game be lost by us? (Modals – To ask the least possibility. “Game” is a receiver. “We” converts into “Us.” “Us” is a doer.)
- Active Voice = I would rather leave than waiting here. (Modals – To express a formal and polite opinion. “I” is a doer.) (“Waiting” is a participle.)
- Passive Voice = It would rather be left than being waited here by me. (Modals – To express a formal and polite opinion. There is no object, so we use “It.” “It” is a receiver. “I” converts into “Me.” “Me” is a doer.) (Be + verb 3rd form = Being waited, Passive Participle)
- Active Voice = You must choose between us. (Modals – To express necessity. “You” is a doer.)
- Passive Voice = It must be chosen between us by you. (Modals – To express necessity. There is no object so, we use “It.” “It” is a receiver. “You” converts into “You.” “You” is a doer.) (Between us – It is a prepositional phrase, not an object.)
- Active Voice = He would never kill you. (Modals – To express strong possibility. “He” is a doer.)
- Passive Voice = You would never be killed by him. (Modals – To express strong possibility. “You” converts into “You.” “You” is a receiver. “He” converts into “Him.” “Him” is a doer.)
- Active Voice = When do you apply? (Present Simple or Present Indefinite Tense – Ask a general truth. “You” is a doer.)
- Passive Voice = When is it applied by you? (Present Simple or Present Indefinite Tense – Ask a general truth. There is no object so we use “It.” “It” is a receiver. “You” converts into “You.” “You” is a doer.)
- Active Voice = How can I play this? (Modals – To ask possibility. “I” is a doer.)
- Passive Voice = How can this be played by me? (Modals – To ask possibility. “This” is a receiver. “I” converts into “Me.” “Me” is a doer.)
- Active Voice = Who sings this song? (Present Simple or Present Indefinite Tense – Ask a general truth. “Who” is a doer.)
- Passive Voice = By whom is this song sung? (Present Simple or Present Indefinite Tense – Ask a general truth. “This song” is a receiver. “Who” converts into “Whom.” “Whom” is a doer.)
Join The Discord If You Have Doubts – Click The Chat Box
Pages: 1 2


